Registering a Business in China
_UPDATED.png)
Registering a business in China can be a long process. In 2017, China was ranked 28th out of 190 countries (1 being the best) for starting a business It takes an average of 4 procedures and 9 days to establish a corporate entity in China.
Business registration processes are often on the economic agenda for the Chinese government. Recently, a spate of Free Trade Zones (FTZs) have been created to provide a number of economic benefits for doing business in certain areas of China, chief amongst which includes simplifying business registration.
Registering IP is another area that the government has targeted for improvement. Despite recent simplifications to the process, some companies reportedly continue to suffer commercial losses due to the difficulty in IP registration. Registering IP rights in China is more expensive and far slower than in Australia. For example, trademarks take 18 months to be granted, design patents six to eight months and copyright recordal procedures three months.
The process of registering a business
The process for registering a business in China depends on the type of business – joint venture, wholly foreign-owned enterprise or representative office. Setting up a business in China overall generally takes three to six months and involves various government authorities and procedures that may differ depending on the industry your business is in and the structure you have chosen. The primary Chinese Government authorities involved are:
- Ministry of Commerce
- State Administration of Industry and Commerce (SAIC)
- State Administration of Foreign Exchange (SAFE)
- State Administration of Taxation
- General Administration of Customs
- State Bureau of Quality and Technical Supervision
- National Bureau of Statistics
The four primary options Australian business can choose from to set up a foreign investment enterprise (FIE) are: representative offices (RO), wholly foreign owned enterprises (WFOE), joint ventures (JVs) – of which there are two types – one being foreign invested partnerships (FIP).
Your business scope should be clearly defined early on in the process of starting a business, as it is what will appear on your business licence in China. Your business can conduct activity es in China only within its business scope. Keep in mind that further application and approval is required if you want to make any amendments to the scope, which can be very time-consuming.
Representative Offices (RO)
The easiest and simplest type of business structure to register in China is a representative office (RO). It is therefore popular with Australian businesses that simply want to get a feel for the Chinese market and environment and make business connections. There are no registered capital requirements for a representative office, but it does have a limited business scope. Under Chinese laws, an RO is not permitted to engage in any remuneration or profit-making activities and cannot issue receipts or accept payment for services. An RO can only partake in market research and public relations activities that directly relate to the business’s products or services, as well as contact activities that relate to provision of the product and domestic procurement and investment.
Other requirements include:
- The parent company must have been established for a minimum of two years.
- It cannot directly hire local employees. Rather, it must engage an official Chinese employment agency.
- The registration certificate is issued for a one year term, subject to annual renewal.
- It cannot restructure into a more comprehensive form of foreign direct investment enterprise.
To establish an RO, the parent company must first apply for a business licence by submitting an application with the SAIC, followed by registration with other relevant authorities. In certain industry sectors, an approval from relevant authorities is required prior to submitting the SAIC application. The SAIC registration process generally takes between three and four months and is quite time-consuming when submitting directly to authorities. Australian businesses may prefer to engage a consulting company that has more in-depth procedural knowledge to submit the application.
All applications must be submitted in Mandarin and additionally can be written in English. Documents in both languages shall have equal validity. Approval permits are usually issued within one month of application submission.
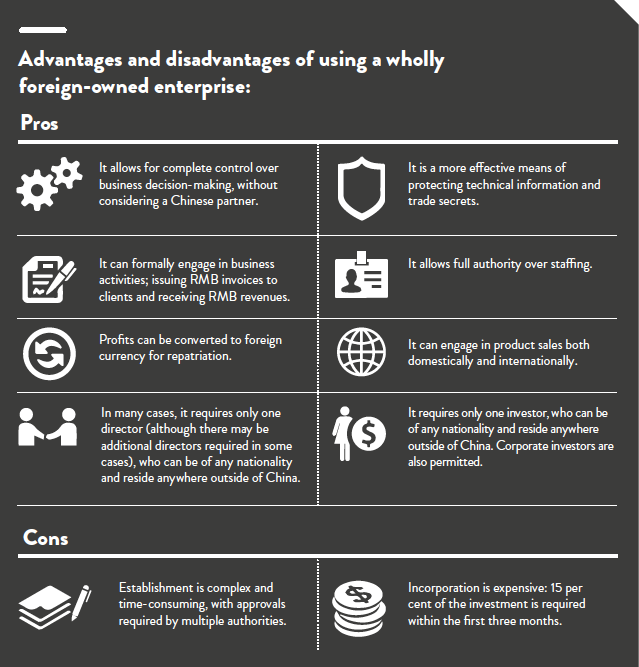
Wholly foreign-owned enterprise (WFOE)
A wholly foreign-owned enterprise (WFOE) is a limited liability company that is entirely funded by one or more foreign entities. WFOE is the most popular business structure chosen by foreign investors as it permits the most freedom in business management. A large amount of capital is required to establish a WFOE but the benefit is that it creates an independent legal entity that can engage in profit-making business, and manage the business in its own way while also allowed to create subsidiaries. A business license is usually issued for 30 years with shorter or longer terms allowed as well as extensions.
It is critical that both the business scope and total investment are accurately defined at the initial application phase to receive government approval as, once established, the WFOE is legally obliged to remain within the parameters of its business scope and meet its financial commitments.
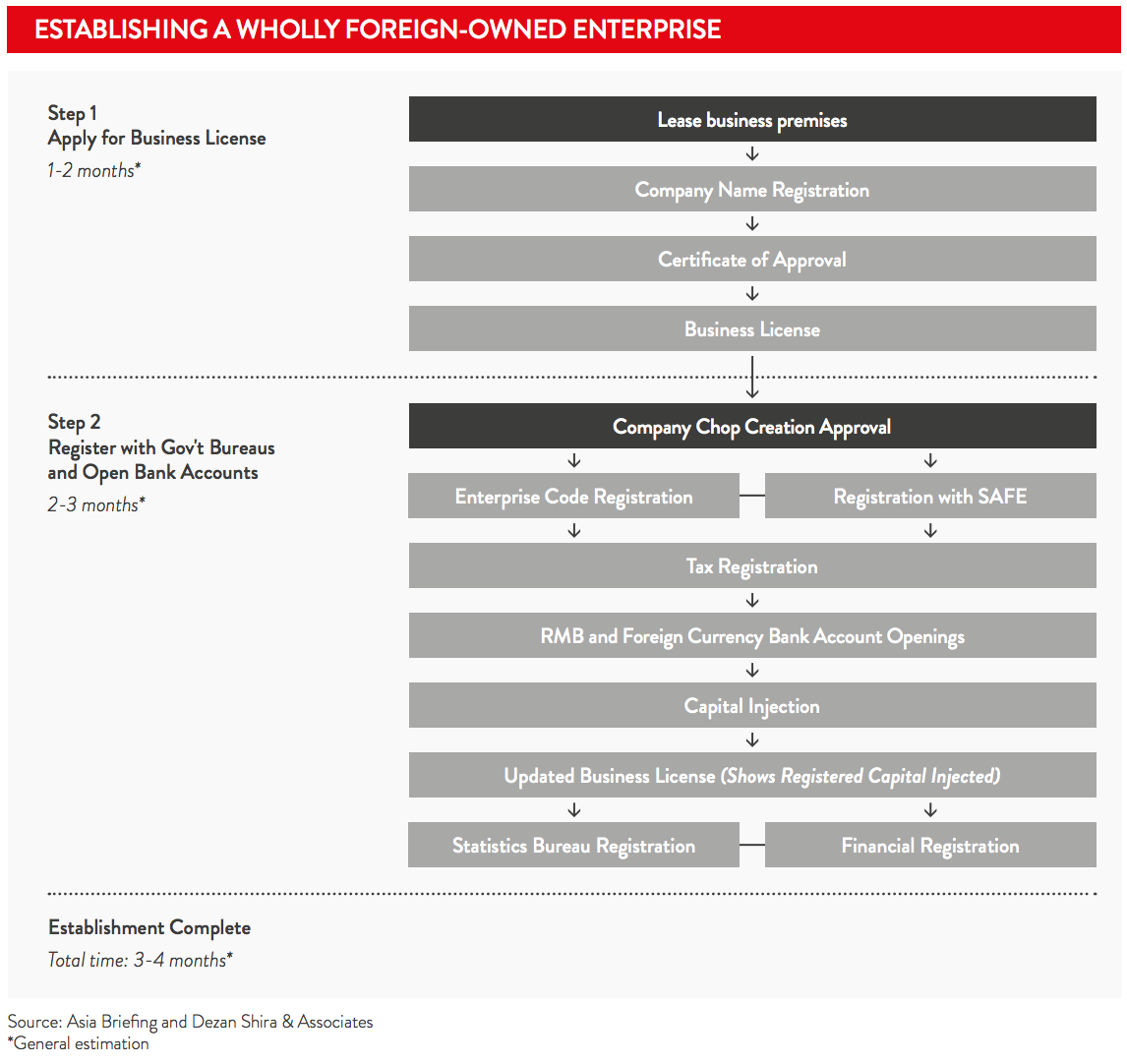
The process of establishing a WFOE in China generally takes between three and four months. An office space must be leased for future business before beginning the WFOE application process. It is recommended that a clause be added to the lease voiding the contract without penalty should the WFOE application be rejected.
The WFOE’s investors must pay 20 per cent of the registered capital within three months of the business licence being issued, with the balance due within two years. The minimum legal requirement is RMB30,000 if the WFOE has two or more investors, or RMB100,000 if the WFOE has only one investor. Authorities, though, will assess on a case-by-case basis the amount of registered capital taking into consideration the proposed business activities and location. The amount is then written into the company’s articles of association.
Joint venture (JV)
A joint venture (JV) is created through a partnership between foreign and Chinese investors, who together share the profits, losses and management of the venture.
For foreign investors, there are two major reasons for choosing to establish a JV; these include government requirements for specific industries, and the local partner being in a beneficial position to assist with market knowledge or established networks. It is strongly recommended that you consult with the foreign partner of an existing JV in order to better understand the advantages and disadvantages of the structure before progressing to establish a JV. Due diligence is essential in choosing the correct partner. See Chapter 4 for further information on due diligence in China.
There are two types of joint ventures in China – equity joint ventures and cooperative or contractual joint ventures, which differ predominantly in the ways in which profits and losses are distributed. Like WFOEs, JVs must pay 15 per cent of the registered capital of the venture within three months of the business licence being issued, with the balance due within the first two years. The same minimum investment requirements and consideration by the Government apply to JVs as WFOEs.
Equity joint venture (EJV)
An equity joint venture (EJV) is the second most common structure used by foreign companies to enter China and the vehicle most preferred by the Chinese Government and Chinese businesses. EJVs are usually established to exploit the market knowledge, preferential market treatment and manufacturing capability of the Chinese side, and the technology, manufacturing knowhow and marketing experience of the foreign partner.
The key to an EJV is the board and management composition. It can be hard to find an organisational structure and shared culture that encompasses Australian reporting and professional requirements, and there are often intellectual property concerns; however, an EJV also allows for full access to the Chinese market and the equal distribution of any profits.
Cooperative or contractual joint venture (CJV)
In a cooperative joint venture, also known as contractual joint venture (CJV), there is no minimum foreign contribution required to initiate the venture, allowing a foreign company to take part in an enterprise where they prefer to remain a minor shareholder. Investors’ contributions are not required to be monetary, and can be ‘in kind’ support such as labour, resources and services. Profit and returns are therefore not based on investment share. Rather, they are divided according to the specific provisions of the joint venture contract. A CJV also allows greater flexibility in the structure of the organisation, management and assets. There is a duration limit for CJVs, although contracts may be renewed subject to the consent of the parties involved and approval from the examination and approval authorities. The foreign investor is also permitted to withdraw all or a portion of their registered capital from the CJV during the duration of the CJV contract.
Foreign-investment partnerships (FIPs)
There are two other foreign investment options that you may consider for setting up a business in China. Foreign-invested joint stock companies (otherwise known as foreign-invested companies limited by shares) are not very common in China and tend to be for larger organisations. The other is the recently introduced foreign-invested partnership (otherwise referred to as a general partnership or limited partnership). FIPs have different benefits not offered by WFOE, including a set-up process without registered capital verification, tax savings, the options of domestic and foreign ownership (both corporate and individual) and hiring of foreigners. The challenge with FIPs is the unlimited liability of the general partner.
Want to learn more? Explore our other China information categories or download the China Country Starter Pack.
