Korea’s imports
Focusing on inbound trade from Korea, the nation is Australia’s ninth largest foreign source of goods and services, with imports totalling over AUD 13 billion in 2015-16. The primary imports from Korea are refined petroleum, passenger motor vehicles, and pumps and associated parts.
Tariffs/Import duties
Korea has a two-column tariff scheme based on the international ‘harmonised system’. Duties are 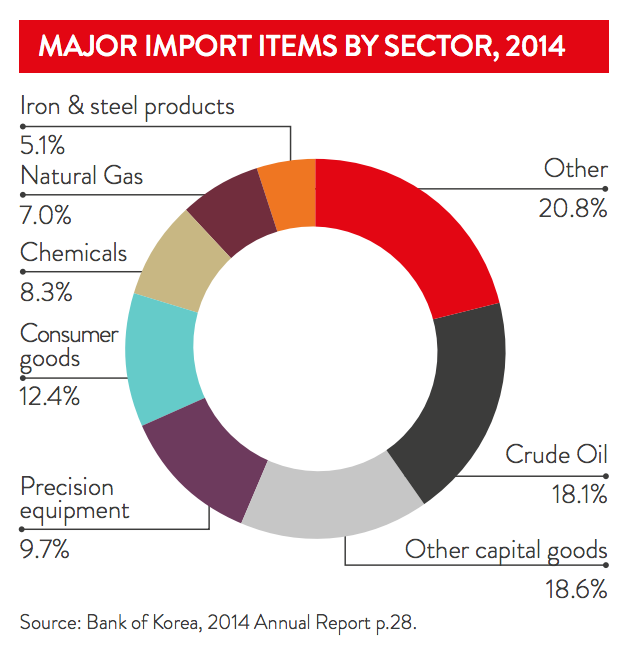 mainly a percentage of the cost, insurance and freight (CIF) value, provided such value is based on current domestic value at date of export. Goods that meet the KAFTA preferential rates are subject to the reduction or elimination of tariffs on items originating from Australia.
mainly a percentage of the cost, insurance and freight (CIF) value, provided such value is based on current domestic value at date of export. Goods that meet the KAFTA preferential rates are subject to the reduction or elimination of tariffs on items originating from Australia.
Other Import duties
For items that are not covered under KAFTA, there are a variety of other applicable import duties across various goods. These are often referred to in the Korean context as “custom duties”.
Customs valuation
The dutiable value of imported goods includes the cost of the goods as well as insurance and freight (CIF). In 2008, the Korea Customs Service introduced the Advanced Customs Valuation Arrangement (ACVA), which provides a mechanism for taxpayers and the customs service to agree to an appropriate dutiable value of imported goods sourced from related parties.

Exemption or abatement
The following goods may be exempt from or eligible for reduction in customs duties:
- Goods for diplomats, government use and academic research
- Foreign goods for use in the defence industry and environmental pollution control
- Raw materials for the production of aircrafts
- Goods to be re-exported
- Deteriorated or damaged goods
- Re-imported goods
Refunds
With goods intended for use in the manufacturing or processing of goods to be exported, and for which customs duties have already been paid at the time of importation, duties will be refunded up to the limit of the amount of customs duties previously paid.
Indirect tax
A flat 10 per cent value-added tax (VAT) is imposed on all imports unless customs duties on such imports are exempt. An individual excise tax of five to 20 per cent is also levied on the import of automobiles and certain luxury items. Rates vary depending on the type of product. Tariffs and taxes must be paid within 15 days after goods have cleared customs.
Taxable value and exemption
The taxable value of imported goods is equal to the total amount of the transaction value for customs duties, individual excise tax and liquor tax (if any). The following goods, on which customs duties are exempt, may also be exempt from VAT:
- Goods imported as commodity samples and advertising materials
- Goods re-imported after export
- Goods imported temporarily under the terms of re- export
- Duty-free goods.
Additionally, under the Special Tax Treatment Control Law (STTCL), a qualified foreign invested corporation may be exempt from customs duties, individual excise tax and VAT on capital goods imported by such companies or contributed in-kind by a foreign investor.
Import regulations
The Korean Government requires that all importers have a general licence or a special licence for all imported items. Import licence applications are administered by government agencies or by the relevant industrial associations after performing screenings. Each specific licence covers only one transaction and is necessary in order to secure credit letters. The Ministry of Strategy and Finance is required to pre-approve imports that are to be exempt from customs duties. Restrictive regulations govern the content and safety of products. Some consumer goods such as food, pharmaceuticals and toys are subject to more stringent examination.
Import requirements and documentation
The documents necessary to obtain import permission vary depending on the type of product, its origin and the type of business in which the applicant is engaged. The following is a summary of the basic documents and information necessary to apply for an import permit.
- A completed application form for an import permit
- Lading bill
- Invoice containing a description of goods, brand name, quantity, specifications, type or model number, unit price, freight, insurance and expenses, as well as any amount of duty reduction or exemption of duties
- Origin verification requirements must be obtained at the port of shipment.
- Packing list
- Price declaration
- Other import documents, such as those covering applications for preferential treatment of goods.
Parallel imports
Parallel imports (often known as grey product) are non-counterfeit products imported from another country without the permission of the intellectual property owner, but which may be allowed due to the concept of exhaustion of rights. While there is no rule on parallel imports of foreign brand goods, Korea has dealt with such imports through a government notice on the export/import clearance guidelines for the protection of intellectual property since 1995. Exclusive licensors or dealers of imported goods may request the customs office to withhold the import customs clearance of parallel import goods. In response to such a request, parallel importers may request the customs office to examine whether such a request may be repealed and the customs office must notify the examination result in 15 days from the date the request is filed. The customs office is empowered to prohibit imports or exports of goods infringing intellectual property rights such as trademarks, copyrights and geographical identification.
Want to learn more? Explore our other South Korea information categories or download the Korea Country Starter Pack.
